ADVANCES IN TOTAL KNEE REPLACEMENTS
Done by Dr Andre Morrish
Arthritis of the knee is a debilitating condition. Osteoarthritis, degeneration of the articular cartilage, is the primary cause usually resulting from previous traumatic injury to the menisci (knee shock absorbers) or ligaments. Other causes are age, bone anomalies (crooked knees), gout and weight.
Signs and symptoms include swelling, clicking, grinding and joint pain. Stiffness and fixed flexion contractures occur with more advanced arthritis.
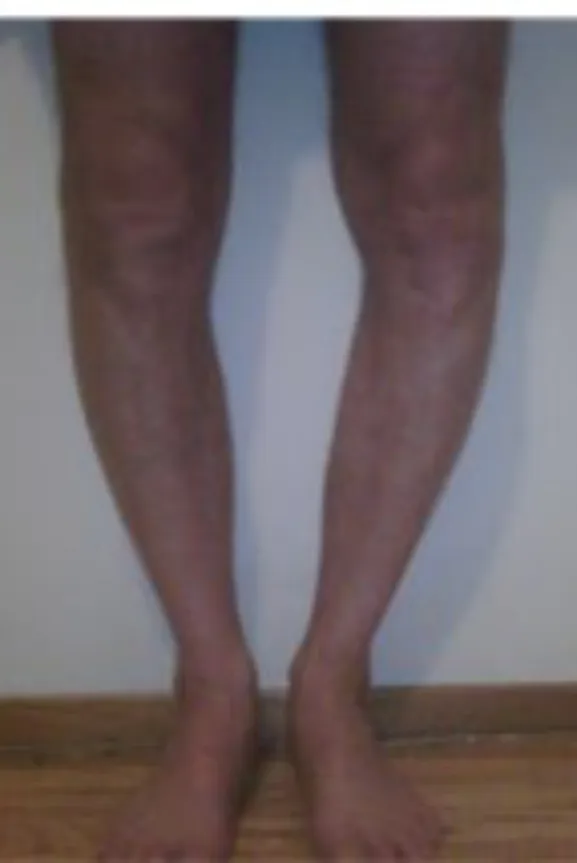
Varus (Bowleg) and Valgus (knock kneed) are common deviations
Diagnosis is made following an examination and x-rays.
SURGICAL TREATMENT:
- Conservative -> Weight loss, anti-inflammatories, Glucosamine injections.
ARTHROSCOPIC DEBRIDEMENTS:
Not bone on bone on x-ray.
Debridement of menisci and removal of loose bodies.
Radio frequency (RF) and micro-fracture.
R.F. -> melts the loose articular cartilage margins to stabilise the defect and prevent progression.
Micro-fracture -> punch small holes into the full thickness chondral defect to promote bone marrow and secondary Fibro cartilage formation.
Partial knee replacements:
Medial bone on bone arthritis; no damage to the lateral joint, patella femoral joint and an intact Anterior cruciate ligament (ACL).
Re-surfacing of the medial compartment.
Keeps your own ligaments.
This is the most natural feeling knee replacement (can do in +- 20% of all arthritic patients)
90% of patients are very satisfied after having a partial knee replacement.
Total knee replacements:
Replace all three compartments. A total knee replacement is done in far more advanced arthritis.
97%- 10-year survival, 80% – 20-year survival.
80% of patients are satisfied with total knee replacements.
Due to 20% of total knee replacement patients being unsatisfied worldwide, there has recently been a drive to understand why and how to prevent this.
Computer aided surgery (CAS)
CAS was introduced in 2005. This allowed precise bony cuts within 1mm as well as soft tissue tensioning. Between 2005 and 2015 I performed hundreds of these CAS procedures but eventually had to stop as the medical aid’s did not fund the extra costs and there was no proof of better outcomes.
Robotic Surgery
The same as CAS but a robotic arm aids in cutting the bone.
Robotic surgery is being driven by industry. Reduces “outliers” – badly performed knee replacements, still no overall improvement in satisfaction.
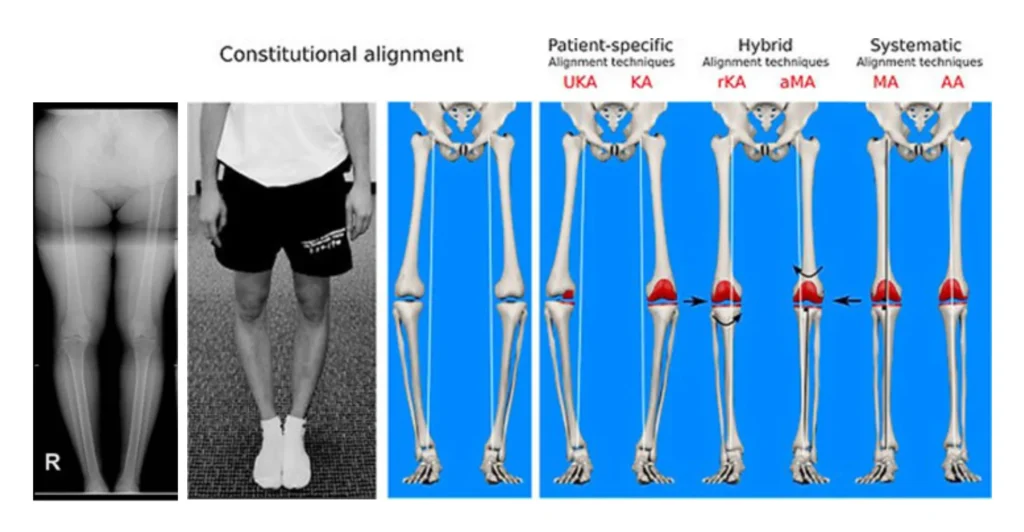
Coronal Plane Alignment of knee (CPAK)
Described recently by Bellemans. Constitutional Alignment (Varus/Valgus) and joint line obliquity (angle of your jointline relative to the floor) are used to determine the ideal placement of the total knee replacement. A long leg standing x-ray is needed to determine these angles. No further costs are incurred!
I’ve recently adopted this strategy for my knee replacements, and I am astonished at the improvement in pain scores and functional scores.
This is the future of knee replacements not Robotics.